Sheath Flow Cell
Flow cytometers have been widely used to characterize biological cells, DNA, and proteins. Recently, complex pre- and post- treatment procedures such as separation, staining and sorting of sample cells are combined with one analyzer. In order to reduce the cost and improve the usability of such devices, flow cytometer and pre- and post-treatment can be integrated into one micro-fluidic chip.
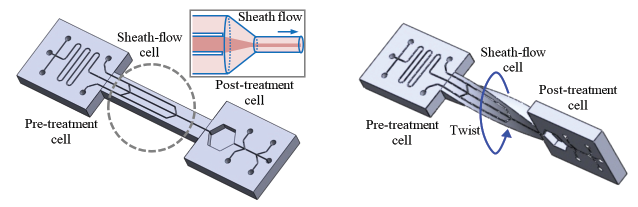
Schematic representation of integrated microfluidic chip for flow cytometry (left). Image of microfluidic chip with twisted microchannels.
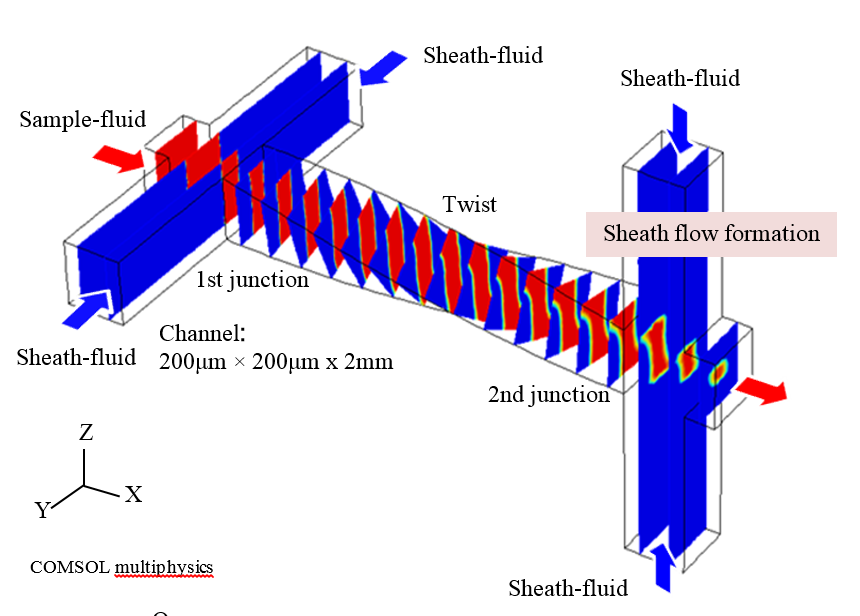
We propose a new structure to generate 3-dimensional focusing flow by using a unique material property of polydimetylsiloxane (PDMS), that is elasticity. We developed a twisted microchannel in order to form a sheath flow in an integrated microfluidic chip. The new device has a central straight channel and two parts of 2-dimensional merging channel. It is twisted by 90 degree in between the first part and the second part.
We have checked the feasibility of our proposed idea by numerical simulation.
The sample fluid goes into the central microchannel with two junction points. In each junction point, the sheath fluids sandwich the sample.
In the first junction point, the sample stream is compressed to rectangular cross section by Y directional sheath flow. Then the sample moves downward through the twisted microchannel and keeps the shape and the direction. In the second junction point, the sample fluid is compressed again by Z directional sheath flow and finally it forms a compressed stream in the center of the channel.
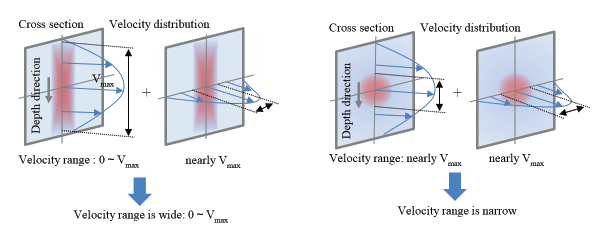
The micro-channel configuration (width, length etc.) were designed to form an isotropic focusing flow. Distribution of particle velocity in the outlet section of the chip shows formation of the sheath flow.